Project update — 26 Jan 2021
ASTRABAT partner Daikin has completed a number of studies to develop a solid electrolyte polymer for high voltage cathodes. The results will be used for the design of the ASTRABAT battery cell
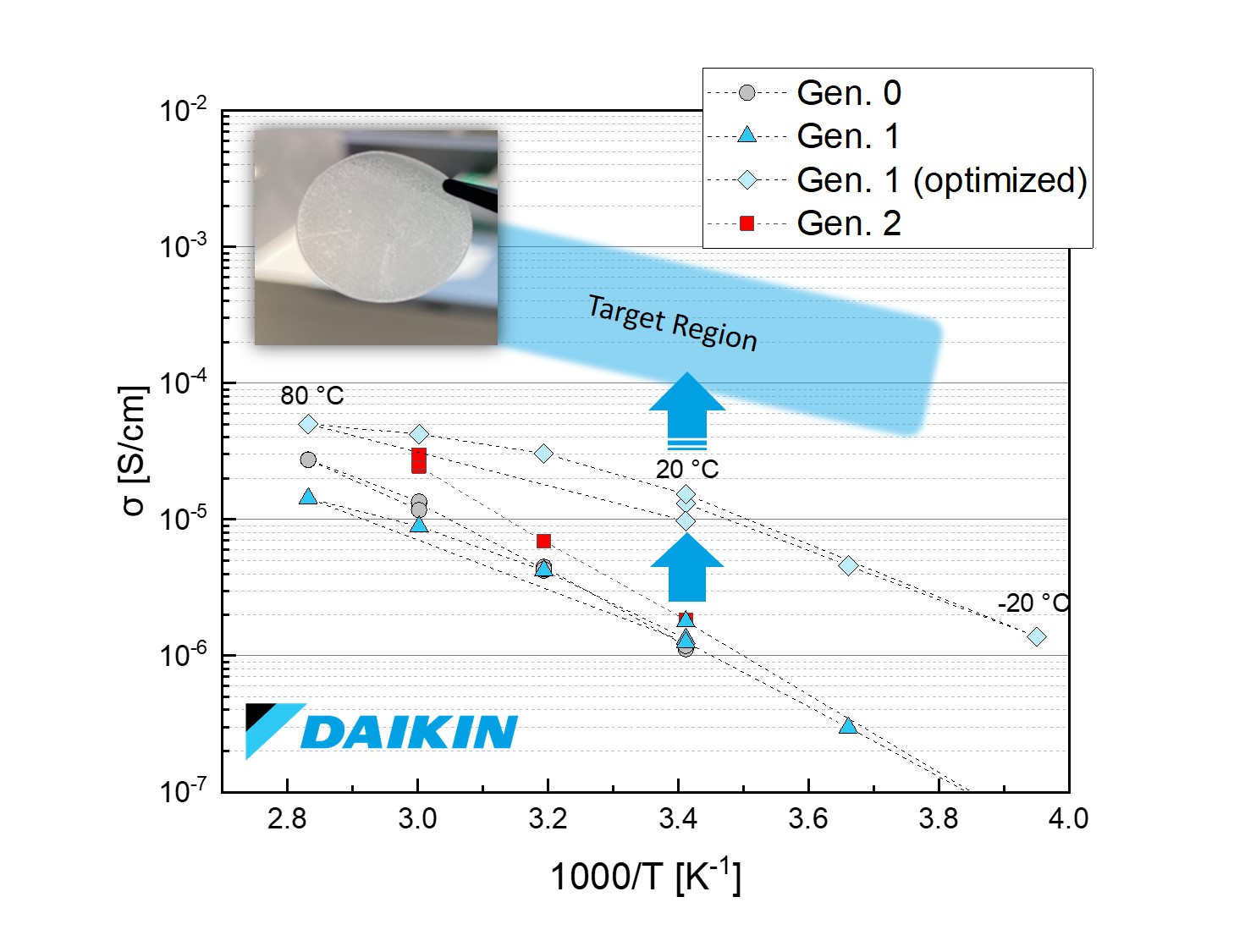
Daikin Chemical Europe GmbH has finalised a series of benchmarking experiments as part of its activity in the ASTRABAT project. These experiments will lead to the development of a polymer suitable for use as a catholyte inside high-voltage cathodes. The polymer’s unique properties will enable high energy density cathode materials to be used inside the ASTRABAT solid state cell.
The experiments play a crucial role in the project, as the performance of all the polymer electrolytes developed will be assessed against the benchmark system. A two-fold development strategy on material level was adopted for the development, focusing on: (i) the modification of the benchmark polymer via the production of composite materials with other polymers, and (ii) the use of complex prototype polymers adapted for the specific application. This two-fold approach shows promising results based on the work performed in the first year of the project.
Daikin is also working on (i) the formulation of the hybrid electrolyte for the ASTRABAT cell prototype, and (ii) the development of processes for commercially producing next-generation solid state cells. The formulation studies were particularly relevant for developing the electrolyte, which now shows a significant conductivity increase compared to the benchmark system.